{Tool} Indirect regulation of aphids in organic stone fruit orchards with natural enemies (BIOFRUITNET Practice Abstract). Creator(s): Boutry, Clémence. Issuing Organisation(s): FiBL - Research Institute of Organic Agriculture. Biofruitnet Practice Abstract, no. 070b. (2022)
|
PDF
- Published Version
- English
(Indirect regulation of aphids in organic stone fruit orchards with natural enemies)
584kB | |
|
PDF
- Published Version
- German/Deutsch
(ndirekte Regulierung von Blattläusen im ökologischen Steinobstanbau mit natürlichen Feinden)
584kB | |
|
PDF
- Published Version
- French/Francais
(Régulation indirecte des pucerons dans les vergers de fruits à noyau bio grâce à des ennemis naturels)
595kB | |
![[thumbnail of 2023-04-21 16_06_03-Protokoll.png]](/44730/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/2023-04-21%2016_06_03-Protokoll.png) 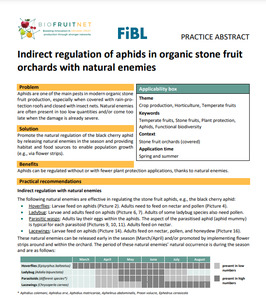 Preview |
Image (PNG)
- Cover Image
- English
87kB |
Document available online at: https://orgprints.org/44730
Summary in the original language of the document
Aphids can be regulated without or with fewer plant protection applications, thanks to natural enemies.
Practical recommendations
Indirect regulation with natural enemies
The following natural enemies are effective in regulating the stone fruit aphids, e.g., the black cherry aphid:
• Hoverflies: Larvae feed on aphids (Picture 2). Adults need to feed on nectar and pollen (Picture 4).
• Ladybug: Larvae and adults feed on aphids (Picture 6, 7). Adults of some ladybug species also need pollen.
• Parasitic wasps: Adults lay their eggs within the aphids. The aspect of the parasitised aphid (aphid mum-my) is typical for each parasitoid (Pictures 9, 10, 11). Adults feed on nectar.
• Lacewings: Larvae feed on aphids (Picture 14). Adults feed on nectar, pollen, and honeydew (Picture 16).
These natural enemies can be released early in the season (March/April) and/or promoted by implementing flower strips around and within the orchard.
| EPrint Type: | Practice tool |
|---|---|
| What problem does the tool address?: | Aphids are one of the main pests in modern organic stone fruit production, especially when covered with rain-protection roofs and closed with insect nets. Natural enemies are often present in too low quantities and/or come too late when the damage is already severe. |
| What solution does the tool offer?: | Promote the natural regulation of the black cherry aphid by releasing natural enemies in the season and providing habitat and food sources to enable population growth (e.g., via flower strips). |
| Country: | Switzerland |
| Type of Practice Tool: | Practice abstracts |
| Keywords: | Temperate fruits, Stone fruits, Plant protection, Aphids, Functional biodiversity |
| Agrovoc keywords: | Language Value URI English temperate fruits http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_7655 English stone fruits http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_25461 English plant protection http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_5978 English Aphidoidea http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_30757 English biodiversity http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_33949 |
| Subjects: | Crop husbandry > Production systems > Fruit and berries Crop husbandry > Crop health, quality, protection |
| Research affiliation: | European Union > Horizon 2020 > Biofruitnet Switzerland > FiBL - Research Institute of Organic Agriculture Switzerland > Crops > Special crops > Fruit European Union > Organic Farm Knowledge |
| Horizon Europe or H2020 Grant Agreement Number: | 862850 |
| Related Links: | https://organic-farmknowledge.org/tool/44730, https://organic-farmknowledge.org/tool/44729, https://biofruitnet.eu |
| Project ID: | ofk |
| Deposited By: | Basler, Andreas |
| ID Code: | 44730 |
| Deposited On: | 10 Dec 2022 09:36 |
| Last Modified: | 11 Sep 2024 11:00 |
| Document Language: | English, German/Deutsch, French/Francais |
| Status: | Published |
Repository Staff Only: item control page

 Download Statistics
Download Statistics Download Statistics
Download Statistics
