{Tool} Nitrogen supply for winter oilseed rape (OK-Net Arable Practice Abstract). [Stickstoffversorgung im Winterrapsanbau.] Creator(s): Daniel, Claudia; Dierauer, Hansueli; Clerc, Maurice; Conder, Malgorzarta and Weidmann, Gilles. Issuing Organisation(s): FiBL - Research Institute of Organic Agriculture. OK-Net Arable Practice Abstract, no. 009. (2017)
Preview |
PDF
- German/Deutsch
(Stickstoffversorgung von Winterraps)
714kB |
Preview |
PDF
- English
(Nitrogen supply for winter oilseed rape)
439kB |
![[thumbnail of 2022-09-05 11_10_18-Nitrogen supply for winter oilseed rape.png]](/31024/25.hassmallThumbnailVersion/2022-09-05%2011_10_18-Nitrogen%20supply%20for%20winter%20oilseed%20rape.png) 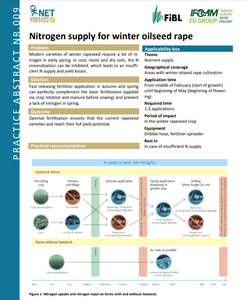 Preview |
Image (PNG)
- Cover Image
- English
194kB |
Document available online at: https://orgprints.org/31024/
Summary in the original language of the document
Optimal fertilisation ensures that the current rapeseed varieties and reach their full yield potential.
Practical recommendation
• In conventional cultivation, the nitrogen uptake of winter oilseed rape amounts to 140 kg N per ha for a yield expectation of 35 dt per ha. In organic agriculture, about 100 kg suffice for a yield expectation of 20-25 dt.
• The ideal time for cultivating oilseed rape is after grass-clover or legumes. After grains, apply about 30 tonnes per ha of manure or manure compost before cultivating rapeseed.
• In dry conditions in spring, an early single application of nitrogen is preferable to two smaller applications. In the case of slurry with a low N content, two applications are often required because maximum of 40 m3 of slurry can be applied at once. Regularly analyse the N content of slurry (regular content: 1 kg of N per m3 of slurry or tonne of manure, respectively; range: 0, 3 kg N per m3 for cow slurry to 3 kg N per m3 for pig slurry). The N contents of commercial fertiliser and liquid digestate are disclosed by the suppliers.
• On farms without livestock, one dose of organic commercial fertiliser is applied in early spring.
Summary translation
Eine optimale Düngung stellt sicher, dass die heutigen Rapssorten ihr Ertragspotenzial entfalten können.
Vorgehen
• Im konventionellen Anbau liegt der N-Bedarf von Winterraps bei einer Ertragserwartung von 35 dt/ha bei 140 kg N/ha. Im Bioanbau reichen bei einer Ertragserwartung von 20-25 dt/ha 100 kg N/ha aus.
• Raps idealerweise nach Kleegras oder Leguminosen anbauen. Bei Anbau nach Getreide vor der Rapssaat etwa 30 t/ha Mist oder Mistkompost ausbringen.
• Bei trockenen Verhältnissen im Frühjahr den Stickstoff besser in einer einzigen, frühen Gabe als in zwei kleineren Gaben verabreichen. Bei Gülle mit einem geringen N-Gehalt sind meist zwei Gaben nötig, da pro Gabe maximal 40 m3 Gülle ausgebracht werden können. Den N-Gehalt der Gülle regelmässig analysieren lassen (Normalgehalt: 1 kg N pro m3 Gülle bzw. t Mist; Spannbreite: 0,3 kg N/m3 bei Rinder-Laufstallgülle bis 3 kg N/m3 bei Schweinegülle). Die N-Gehalte von Handelsdüngern und Presswasser werden vom Lieferanten mitgeteilt.
• In viehlosen Betrieben wird mit einer Gabe organischem Handelsdünger im sehr frühen Frühjahr gedüngt.
| EPrint Type: | Practice tool |
|---|---|
| What problem does the tool address?: | Modern varieties of winter rapeseed require a lot of nitrogen in early spring. In cool, moist and dry soils, the N mineralisation can be inhibited, which leads to an insufficient N supply and yield losses. |
| What solution does the tool offer?: | Fast releasing fertilizer application in autumn and spring can perfectly complement the basic fertilisation (applied via crop rotation and manure before sowing) and prevent a lack of nitrogen in spring. |
| Country: | Switzerland |
| Type of Practice Tool: | Practice abstracts |
| Location: | Areas with winter oilseed rape cultivation |
| Theme: | Nutrient management |
| Keywords: | arable farming, crop species, nutrient management |
| Keywords: | arable farming, crop species, nutrient management |
| Agrovoc keywords: | Language Value URI English arable farming http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_36528 English crops http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_1972 English nutrient management http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_330697 English oil crops http://aims.fao.org/aos/agrovoc/c_5328 |
| Subjects: | Crop husbandry > Production systems > Cereals, pulses and oilseeds Crop husbandry > Composting and manuring Farming Systems > Farm nutrient management |
| Research affiliation: | European Union > Horizon 2020 > OK-Net Arable > OK-Net-Arable Tools Switzerland > FiBL - Research Institute of Organic Agriculture Switzerland > Knowledge exchange > Advice European Union > Horizon 2020 > OK-Net Arable European Union > Organic Farm Knowledge |
| Horizon Europe or H2020 Grant Agreement Number: | 652654 |
| Related Links: | https://organic-farmknowledge.org/tool/31024 |
| Project ID: | ofk |
| Deposited By: | Forschungsinstitut für biologischen Landbau, FiBL |
| ID Code: | 31024 |
| Deposited On: | 18 Jan 2017 13:24 |
| Last Modified: | 02 May 2024 10:31 |
| Document Language: | English, German/Deutsch |
| Status: | Published |
Repository Staff Only: item control page

 Download Statistics
Download Statistics Download Statistics
Download Statistics
